Hooks规则
React Hooks的使用,有两个规则:
- Hooks只能在函数组件中使用;
- 不能在条件、循环或者嵌套函数中使用hook。确保每一次渲染中都按照同样的顺序被调用,
import React, { useState } from "react";
export default function PersonalInfoComponent() {
const [name, setName] = useState("读心悦");
const [career, setCareer] = useState("前端");
return (
<div className="personalInfo">
<p>姓名:{name}</p>
<p>职业:{career}</p>
<button
onClick={() => {
setName("duxinyues");
}}
>
修改姓名
</button>
</div>
);
}
这一段代码中的hook是按照正常的顺序来执行的,现在把hook放到条件语句中:
import React, { useState } from "react";
let isMounted = false;
export default function PersonalInfoComponent() {
let name, career, setName;
console.log("isMounted", isMounted);
if (!isMounted) {
// eslint-disable-next-line
[name, setName] = useState("读心悦");
// if 内部的逻辑执行一次后,就将 isMounted 置为 true(说明已挂载,后续都不再是首次渲染了)
isMounted = true;
}
[career] = useState("前端开发");
console.log("career", career);
return (
<div className="personalInfo">
<p>姓名:{name}</p>
<p>职业:{career}</p>
<button
onClick={() => {
setName("duxinyues");
}}
>
修改姓名
</button>
</div>
);
}
这段代码,在首次渲染的时候,是可以正常显示。当我们点击修改按钮后,react就会提示报错:
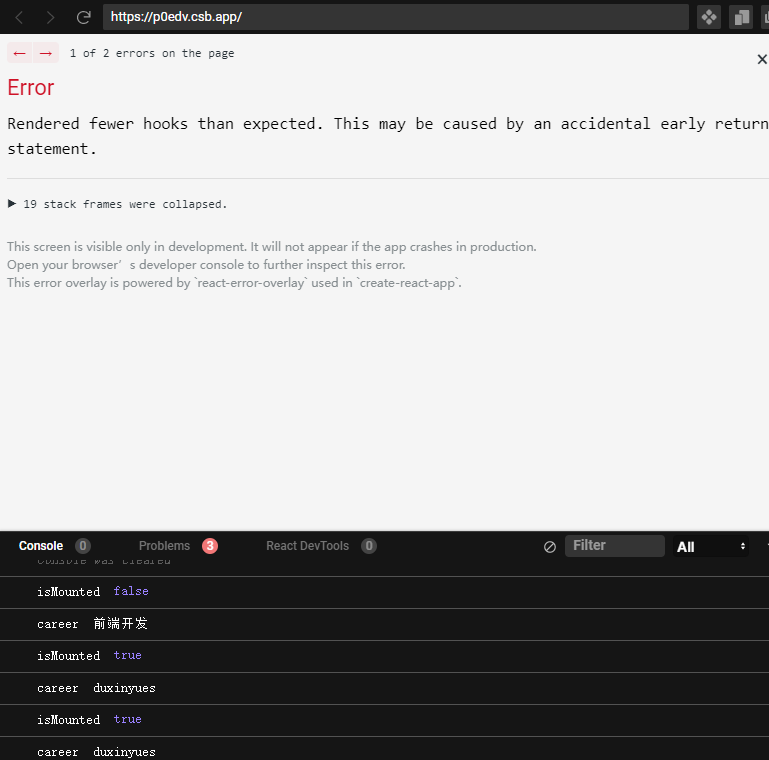
从控制台中看出,我们明明修改的是name,最后更新的确实career,这就是违反规则的后果,会造成hooks状态紊乱。
Hooks机制
从源码中,看一hooks的源码,其中有一个Dispatcher,是一个对象,不同的hook调用的函数不同。 全局变量ReactCurrentDispatcher.current的赋值是通过判断是首次渲染还是更新阶段赋不同的值:
源码文件ReactFiberHooks.old.js
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
current === null || current.memoizedState === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
hooks在首次渲染和更新阶段是执行不同的逻辑。
HooksDispatcherOnMount代码:
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
useCallback: mountCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: mountEffect,
useImperativeHandle: mountImperativeHandle,
useLayoutEffect: mountLayoutEffect,
useInsertionEffect: mountInsertionEffect,
useMemo: mountMemo,
useReducer: mountReducer,
useRef: mountRef,
useState: mountState,
useDebugValue: mountDebugValue,
useDeferredValue: mountDeferredValue,
useTransition: mountTransition,
useMutableSource: mountMutableSource,
useSyncExternalStore: mountSyncExternalStore,
useslug: mountId,
unstable_isNewReconciler: enableNewReconciler,
};
HooksDispatcherOnUpdate代码:
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
useCallback: updateCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: updateEffect,
useImperativeHandle: updateImperativeHandle,
useInsertionEffect: updateInsertionEffect,
useLayoutEffect: updateLayoutEffect,
useMemo: updateMemo,
useReducer: updateReducer,
useRef: updateRef,
useState: updateState,
useDebugValue: updateDebugValue,
useDeferredValue: updateDeferredValue,
useTransition: updateTransition,
useMutableSource: updateMutableSource,
useSyncExternalStore: updateSyncExternalStore,
useslug: updateId,
unstable_isNewReconciler: enableNewReconciler,
};
useState初次渲染
先看一下useState的源码:
export function useState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
在源码中定义比较简单,先获取当前的dispatcher,再追溯到resolveDispatcher方法,它的源码为:
function resolveDispatcher() {
const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
if (__DEV__) {
if (dispatcher === null) {
....
}
return ((dispatcher: any): Dispatcher);
}
useState在首次渲染,执行的是HooksDispatcherOnMount.useState,也就是mountState方法。再来看一下mountState函数的源码:
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
// 将hook追加到链表尾部
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
// initialState是回调函数的或=话,就获取回调函数执行的返回值
initialState = initialState();
}
// 把initialState保存下来
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue: UpdateQueue<S, BasicStateAction<S>> = {
pending: null,
interleaved: null,
lanes: NoLanes, // 优先级
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
};
hook.queue = queue;
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchSetState.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
mountState函数主要是为了初始化hook。再从mountWorkInProgressHook方法中,了解一下hook的数据结构。源码如下:
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null, // 不同的hook,有不同的值
baseState: null, // 初始state
baseQueue: null, // 初始队列
queue: null, // 需要更新的队列
next: null, // 下一个hook
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
hook的相关信息,是保存在一个对象中,hook对象之间是以单向链表的形式连接。hook则是保存在Fiber的memoizedState上,需要更新的是保存在hook.queue.pending中。
现在可以看出,组件所有的hook之间是以单向链表形式串联,环环相扣。如果链表上的某一个hook丢失了,那么链表的顺序就发生变化,链表上的hook与之前就不能意义对应,从而导致hook状态紊乱。
useState更新渲染
在更新阶段,使用的dispatcher是HooksDispatcherOnUpdate。我们在组件更新的时候,调用的是useState,实际上就是在调用HooksDispatcherOnUpdate.useState,也就是updateState方法,代码如下:
function updateState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, (initialState: any));
}
在源码中,useState和useReducer是复用一套更新机制,由于useReducer的代码有点多,就不贴出来了。
updateState就是按照顺序遍历之前已经构建好了的链表,取出对应的数据信息进行更新。
小总结:
mountState(首次渲染)构建链表并且渲染;
updateState(更新渲染)一次遍历链表并且渲染;
useEffect初次渲染
源码中useEffect的定义如下:
export function useEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): void {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useEffect(create, deps);
}
在初次渲染的时候,调用的是mountEffect,mountEffect又调用的是mountEffectImpl,mountEffectImpl代码如下:
function mountEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps): void {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook(); //获取链表
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps; // 依赖
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags; // 添加flag
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
create,
undefined,
nextDeps,
);
}
mountEffect代码如下:
function mountEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): void {
if (
__DEV__ &&
enableStrictEffects &&
(currentlyRenderingFiber.mode & StrictEffectsMode) !== NoMode
) {
return mountEffectImpl(
MountPassiveDevEffect | PassiveEffect | PassiveStaticEffect,
HookPassive,
create,
deps,
);
} else {
return mountEffectImpl(
PassiveEffect | PassiveStaticEffect,
HookPassive,
create,
deps,
);
}
}
在首次渲染,useEffect也是保存在hook.memoizedState上的。
useEffect更新阶段
在更新阶段,调用的是updateEffect,代码如下:
function updateEffect(
create: () => (() => void) | void,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): void {
return updateEffectImpl(PassiveEffect, HookPassive, create, deps);
}
function updateEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps): void {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
let destroy = undefined;
if (currentHook !== null) {
const prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState;
destroy = prevEffect.destroy;
if (nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps = prevEffect.deps;
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
return;
}
}
}
currentlyRenderingFiber.flags |= fiberFlags;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookFlags,
create,
destroy,
nextDeps,
);
}
浅比较依赖,如果依赖发生变化,那么就需要重新执行了。
useRef
useRef在首次渲染,调用的是mountRef,代码如下:
function mountRef<T>(initialValue: T): {|current: T|} {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook(); // 获取useRef
const ref = {current: initialValue}; //初始化ref
hook.memoizedState = ref;
return ref;
}
在render的时候,带有ref属性的Fiber就会标记上Ref tag。
更新阶段的时候,调用的是updateRef,然后返回hook链表。
function updateRef<T>(initialValue: T): {|current: T|} {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
return hook.memoizedState;
}
useMemo & useCallback
首次渲染useCallback和useMemo的源码:
function mountMemo<T>(
nextCreate: () => T,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): T {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
const nextValue = nextCreate();
hook.memoizedState = [nextValue, nextDeps];
return nextValue;
}
function mountCallback<T>(callback: T, deps: Array<mixed> | void | null): T {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
hook.memoizedState = [callback, nextDeps];
return callback;
}
它们的区别是在memoizedState上存储的是callback还是value。
更新阶段的源码:
function updateMemo<T>(
nextCreate: () => T,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): T {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
const prevState = hook.memoizedState;
if (prevState !== null) {
// Assume these are defined. If they're not, areHookInputsEqual will warn.
if (nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps: Array<mixed> | null = prevState[1];
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
return prevState[0];
}
}
}
const nextValue = nextCreate();
hook.memoizedState = [nextValue, nextDeps];
return nextValue;
}
function updateCallback<T>(callback: T, deps: Array<mixed> | void | null): T {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
const prevState = hook.memoizedState;
if (prevState !== null) {
if (nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps: Array<mixed> | null = prevState[1];
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
return prevState[0];
}
}
}
hook.memoizedState = [callback, nextDeps];
return callback;
}
这就是常用到的hooks的源码以及简单解析。